Unveiling the Power of Monte Carlo Simulation
1 Introduction
Monte Carlo Simulation is a versatile and widely used statistical technique that allows researchers and analysts to model the probability of different outcomes in a process with inherent uncertainty. In this blog post, we will embark on a journey to understand the fundamentals of Monte Carlo Simulation, explore its applications, and provide practical examples using Python.
Monte Carlo Simulation is a statistical method that leverages random sampling to obtain numerical results. It is particularly useful in situations where deterministic models are impractical due to complex interactions and uncertainties. Monte Carlo methods use random sampling to solve deterministic problems. The technique is named after the Monte Carlo Casino, known for its games of chance.
1.1 Applications:
Financial modeling for risk analysis. Simulating physical systems in engineering. Optimizing business processes under uncertainty.
Code
# Simulating the probability distribution of the sum of two six-sided dice rolls
# Number of simulations
num_simulations = 100000
# Simulate two dice rolls num_simulations times
dice_rolls = np.random.randint(1, 7, (num_simulations, 2))
# Calculate the sum of each pair of dice rolls
sum_of_rolls = np.sum(dice_rolls, axis=1)
# Plot the probability distribution
plt.hist(sum_of_rolls, bins=np.arange(1.5, 13.5, 1), density=True, edgecolor='black')
plt.title('Probability Distribution of the Sum of Two Dice Rolls')
plt.xlabel('Sum of Rolls')
plt.ylabel('Probability')
plt.show()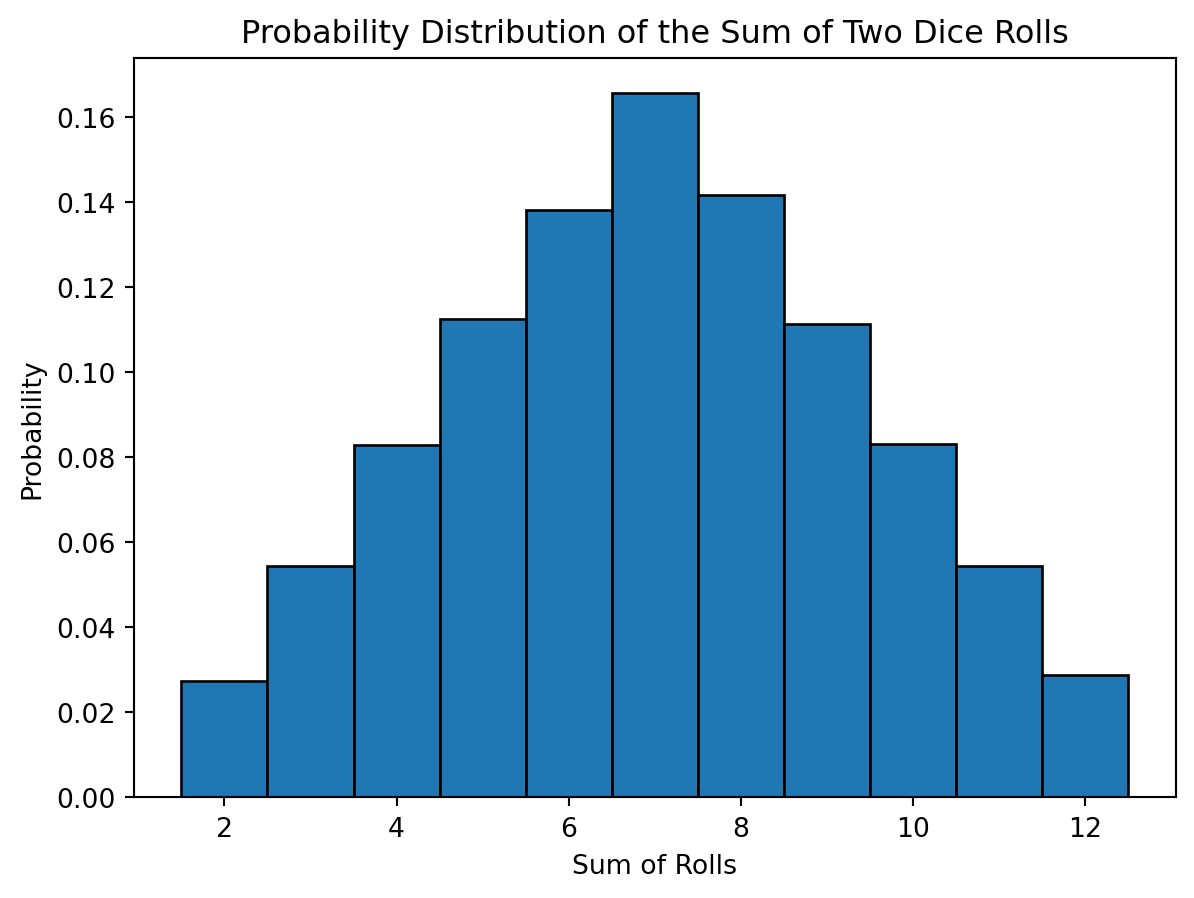
1.2 Applications
Risk Analysis in Finance - Monte Carlo Simulation is extensively used for risk assessment in financial modeling. It helps in understanding the range of possible outcomes and the likelihood of different financial scenarios. Risk analysis assists in making informed investment decisions.
Code
# Financial Monte Carlo Simulation Example
# Simulating future stock prices based on historical data
# Define parameters
initial_price = 100
volatility = 0.2
drift = 0.001
time_horizon = 252 # number of trading days in a year
# Generate random price movements
daily_returns = np.random.normal(loc=(1 + drift) ** (1 / time_horizon), scale=volatility / np.sqrt(time_horizon), size=num_simulations)
# Calculate the stock prices over time
stock_prices = initial_price * np.cumprod(daily_returns)
# Plot the simulated stock prices
plt.plot(stock_prices, color='blue', alpha=0.5)
plt.title('Monte Carlo Simulation of Stock Prices')
plt.xlabel('Trading Days')
plt.ylabel('Stock Price')
plt.show()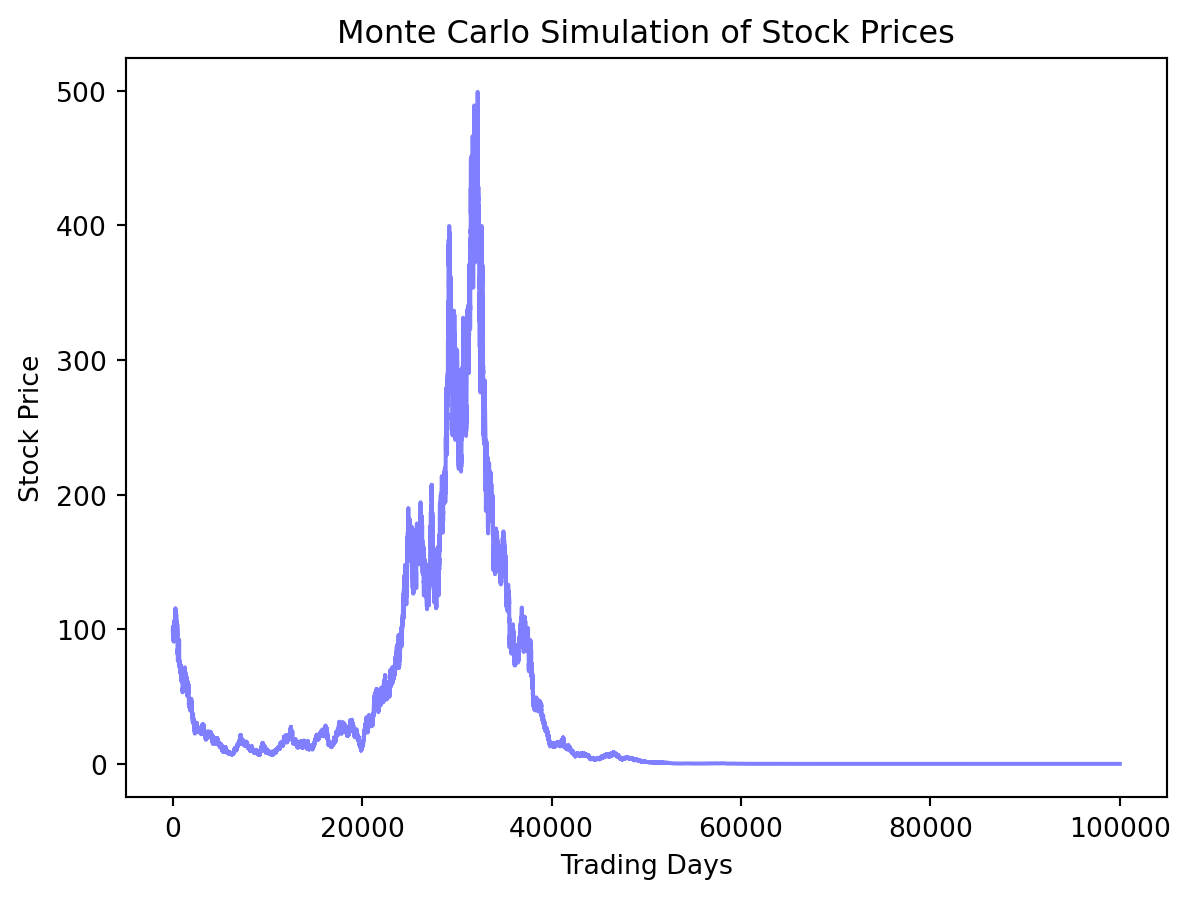
Project Management and Time Estimation Monte Carlo Simulation aids in project management by providing realistic estimates of project timelines. It considers uncertainties and variations in task durations to create a more accurate project schedule. Key Points: Monte Carlo simulations account for variability in project timelines. Project managers can identify critical paths and potential delays. Challenges and Considerations Despite its power, Monte Carlo Simulation has its limitations and challenges. Common challenges include the need for a large number of simulations for accurate results and the assumption of independence among variables. Key Considerations: Ensure input parameters accurately represent the real-world scenario. Be mindful of computational resources when dealing with a large number of simulations. Conclusion Monte Carlo Simulation stands as a valuable tool for decision-makers facing uncertainty in various fields. Its ability to model complex systems and provide probabilistic